The Space--Low Resistance Shock
The above graphic illustrates the major components of the microcirculation. V is a venule, a an arteriole, c a capillary, ps the precapillary sphincters and ava an arterial-venous anastomosis (i.e., a shunt). The precapillary sphincters are modulated by the sympathetic nervous system.
When the Heart performs well but has to pump blood into a dilated peripheral vascular system, low blood pressure results. Common Causes of Widespread Vasodilation are:


*The graphic below illustrates all the types of conditions that can cause anaphylactic shock. Many common allergens in our environment can be life threatening to some people.

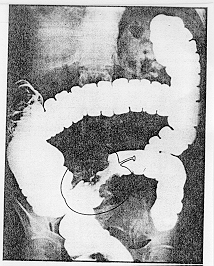
*The above graphic is a barium enema roentgenogram of the colon depicting a surgically resectable annular carcinoma. The stenotic lumen has be likened to the core of an apple. When the above patient has surgery, sepsis will be a constant risk.
3) Sepsis (Widespread blood borne bacterial infection). The most common causes of Sepsis in the ICU environment are tears from abdominal surgery, infected IV lines and a suppressed or compromised immune system. ARDS (Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome) and Sepsis are a particularly lethal combination for the patient. The Mortality rate is between 80-90 % for these patients.
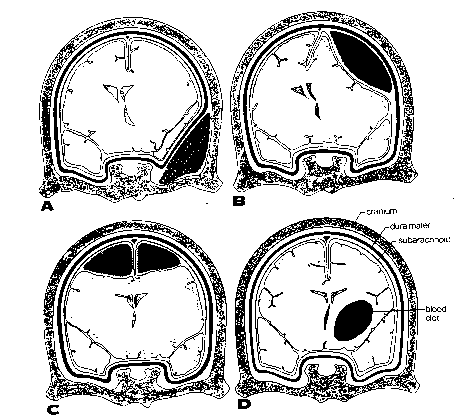
*The above graphic depicts the different types of brain hemorrhages. A shows an extradural hemorrhage while B shows a subdural hemorrhage. Both of these types are relatively easy to evacuate, and the patient's prognosis is good. C shows a subarachnoid hemorrhage while D shows an intracerebral hemorrhage. Both of these are more difficult to evacuate, and the patient's prognosis is poor.
4) Neurogenic Shock-Loss of vasomotor tone due to neurological damage such as head/brainstem injury from trauma or an adverse reaction to anesthesia such as Malignant Hyperthermia.
As venous return to the Heart is held in the dilated peripheral blood vessels, systemic blood pressure begins to fall. The dilated venules and capillaries become more permeable, and the skin becomes Hot and Flushed.
The CVP measurement falls first below 2 mm Hg due to decreased venous return due to the dilated peripheral vessels. The PA falls next followed by the PCWP. The stroke volume is also falling as complete emptying of the Left Ventricle is taking place in an effort to restore the falling Blood Pressure.
Review--Signs of Low Resistance Shock. Falling CVP followed by a falling PA followed by a Falling PCWP. The skin is hot and flushed due to peripheral vasodilation.